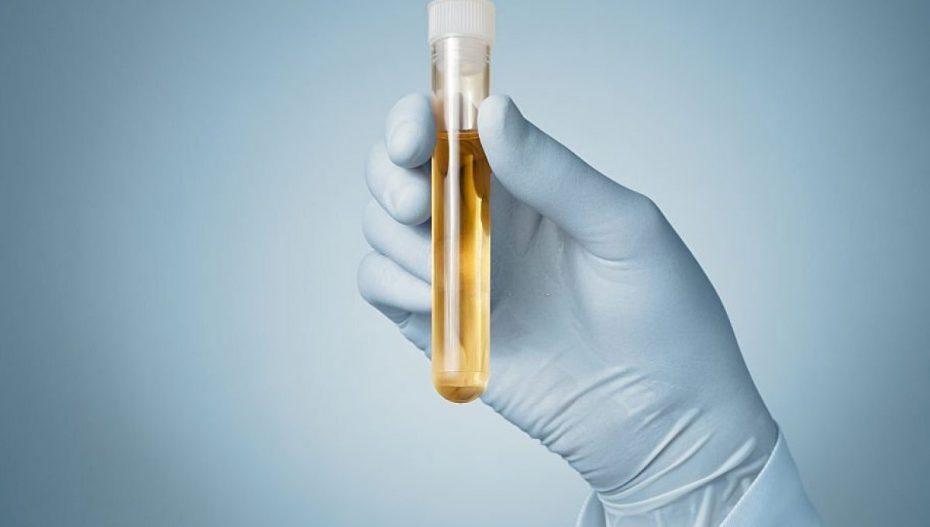
A urine test is a widely used diagnostic tool that provides valuable information about various aspects of your overall health. It can help identify potential issues with major organs, which may impact the color, concentration, and composition of your urine.
A urine test, also referred to as urinalysis, is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide insights into various aspects of your health by analyzing a urine sample. This test can offer valuable information about the cause of certain symptoms and help determine if they are related to existing or potential medical conditions. A urinalysis comprises several examinations that assess the visual, microscopic, and chemical properties of your urine. These examinations enable healthcare professionals to diagnose infections, as well as screen for or monitor common health conditions. Here’s all you need to know about what a urine routine test involves and when it should be done.
When Do You Need a Urine Test?
Urine tests are frequently ordered by doctors for various reasons as a urine sample can provide valuable insights into your health. Your doctor may request a urinalysis for one or more of the following purposes:
- Routine screening to detect early signs of certain health problems.
- Evaluating signs and symptoms associated with diabetes or kidney diseases.
- Monitoring the progress and effectiveness of treatments for conditions like diabetes and kidney diseases.
- Identification and confirmation of a urinary tract infection (UTI).
- It is conducted as a routine assessment of your overall health when you are admitted to a hospital.
- Prior to undergoing surgery, a urinalysis can be part of the preparatory check-up.
What Does a Urine Test Involve?
Consisting of several tests and measurements, the urine test by Apollo comprises 18 different tests. Typically, this test evaluates three different aspects of the urine sample – physical examination, biochemical examination, and microscopic examination.
- Physical Examination:
During a urinalysis, the visual appearance of the urine sample is assessed. It is checked whether it appears cloudy or clear. Also, its color is observed, which can range from pale yellow or colorless to deep amber, depending on the concentration of the urine.
While certain factors like supplements, medications, and foods can influence urine color, an abnormal color could indicate an underlying medical condition. Cloudy urine, for instance, may not always indicate an unhealthy state, but it can be caused by substances such as white blood cells, red blood cells, or bacteria, which may be associated with various medical conditions including:
- Urinary tract infection
- Dehydration
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Diabetes
- Kidney stones
- Biochemical Examination:
Special test strips called dipsticks are used to assess a urine sample’s chemical aspects. Here are some common types of tests conducted using dipsticks during a urinalysis:
- Protein test: It measures the presence of proteins, like albumin, in the urine. Elevated protein levels may indicate various health conditions including kidney issues, heart failure, and dehydration.
- Ketones test: This test detects the presence of ketones, which accumulate when the body breaks down fats for energy. It is often used to screen for diabetes-related ketoacidosis.
- Urine pH level test: A high urine pH may suggest a urinary tract infection or kidney issues, while a low urine pH may indicate conditions like diarrhea or diabetes-related ketoacidosis.
- Glucose test: It measures the amount of sugar in the urine. Normally, glucose should not be present in urine, so its presence could indicate diabetes.
- Nitrite test: A positive nitrite test result suggests a UTI. However, since not all bacteria can convert nitrate to nitrite, even a negative test cannot entirely rule out a UTI.
- Bilirubin test: Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment present in bile, which is produced by the liver. The presence of bilirubin in the urine may indicate bile duct or liver issues.
- Leukocyte esterase test: It detects the presence of leukocyte esterase, an enzyme found in most white blood cells. A positive result may indicate inflammation in the kidneys or urinary tract, often associated with a bacterial UTI.
- Urine-specific gravity test: It measures the concentration of chemical particles in the urine. Abnormal results can provide insights into various health conditions.
- Microscopic Examination:
During urinalysis, a urine sample may be examined under a microscope to identify microscopic substances present. Here are some of the microscopic tests that can be included in a urine routine test :
- Red blood cell (RBC) urine test: Elevated levels of RBCs indicate the presence of blood in the urine. It may suggest issues with the bladder, urinary tract, or kidneys.
- White blood cell (WBC) urine test: Elevated levels of WBCs, along with a positive leukocyte esterase test, may suggest inflammation or infection in the urinary tract.
- Epithelial cells: These cells line the surfaces of the body’s organs and cavities, including the urinary tract. While a small number of epithelial cells in the urine is normal, higher levels may indicate inflammation, infection, or even urinary tract cancer.
- Yeast, bacteria, and parasites: Urine samples can sometimes become contaminated with bacteria, parasites, and yeast. For example, the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis, which causes the sexually transmitted infection trichomoniasis, may be found in the urine of affected individuals.
- Urinary casts: These are tiny tube-like particles formed from proteins released by kidney cells. Different types of casts may indicate various kidney issues. While some casts are normal, others may suggest underlying kidney problems.
If you observe any alterations in your urine, like consistent changes in odor, color, or consistency, it is important to reach out to your doctor. Additionally, if you are experiencing symptoms associated with a UTI, like a burning sensation during urination or a strong and persistent urge to urinate, it is advisable to contact your doctor or visit an urgent care facility. Prompt medical attention can help diagnose and address any potential issues related to your urinary health.